SAME DAY DISPATCH FOR UK/EU DESTINATIONS
SAME DAY DISPATCH FOR UK/EU DESTINATIONSFor a connector design to perform in different harsh environments and applications the materials selected are critical to their operation. Connector shells are often metal and can be aluminium, stainless steel, brass, titanium, or
even composite to meet the demanding harsh environment conditions.
Common Connector Materials
Aluminium
Effective for the majority of interconnect applications, as satisfies both environmental and interconnect requirements. Aluminium is strong, lightweight, corrosion resistant and cost effective, with a variety of surface finishes available to enable it to satisfy various
application requirements and environments.
Nickel Aluminium Bronze
Ideal for marine applications where traditional plating finishes can quickly be eroded by sand and dust revealing weaker base materials, whereas Nickel Aluminium Bronze will remain robust in the harshest of environments.
Stainless Steel
Corrosion resistant steel (CRES) available in 303, 304 and 316 grades, offers excellent corrosion and chemical resistance plus it is stronger than aluminium and needs no additional plating. More expensive than aluminium by 3 to 4 times depending on the grade of material.
Brass
Brass is corrosion resistant by design and being relatively soft, machines easily. It has the added advantage of being a non-sparking metal. Brass does not require additional surface treatment but it is often nickel and chrome plated for increased hardness, wear resistance and enhanced appearance.
Composite
Key advantages over alternative materials include lightweight, superior corrosion resistance and can be a lower cost when manufactured in high volumes. Manufacturers can also plate composites for increased surface hardness and conductivity.
Titanium
Often specified where corrosion resistance and weight are of paramount importance. Titanium is also used in high-temperature environments. Substantially higher in cost than aluminium components.
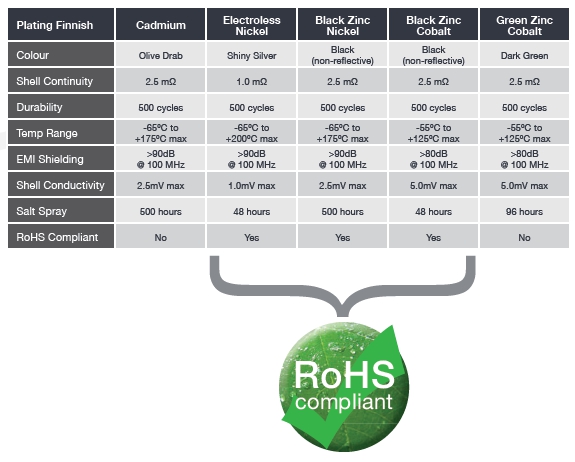
Common Plating Finishes
Cadmium
The historical standard finish of military and industrial connectors offering excellent salt spray corrosion resistance but falls foul of RoHS compliance legislation.
Electroless Nickel
Commonly used on industrial and high-temperature applications, where a nonreflective finish and high corrosion resistance is not important.
Black Zinc Nickel
The latest RoHS-compliant solution to environmental plating of connectors, offering high levels of compatibility with other plating materials.
Nickel PTFE
A lower cost alternative to Black Zinc Nickel. However, the average bath lifetime of the chemical nickel PTFE is half that of electroless nickel and ten times less than nickel alloy (zinc-nickel).